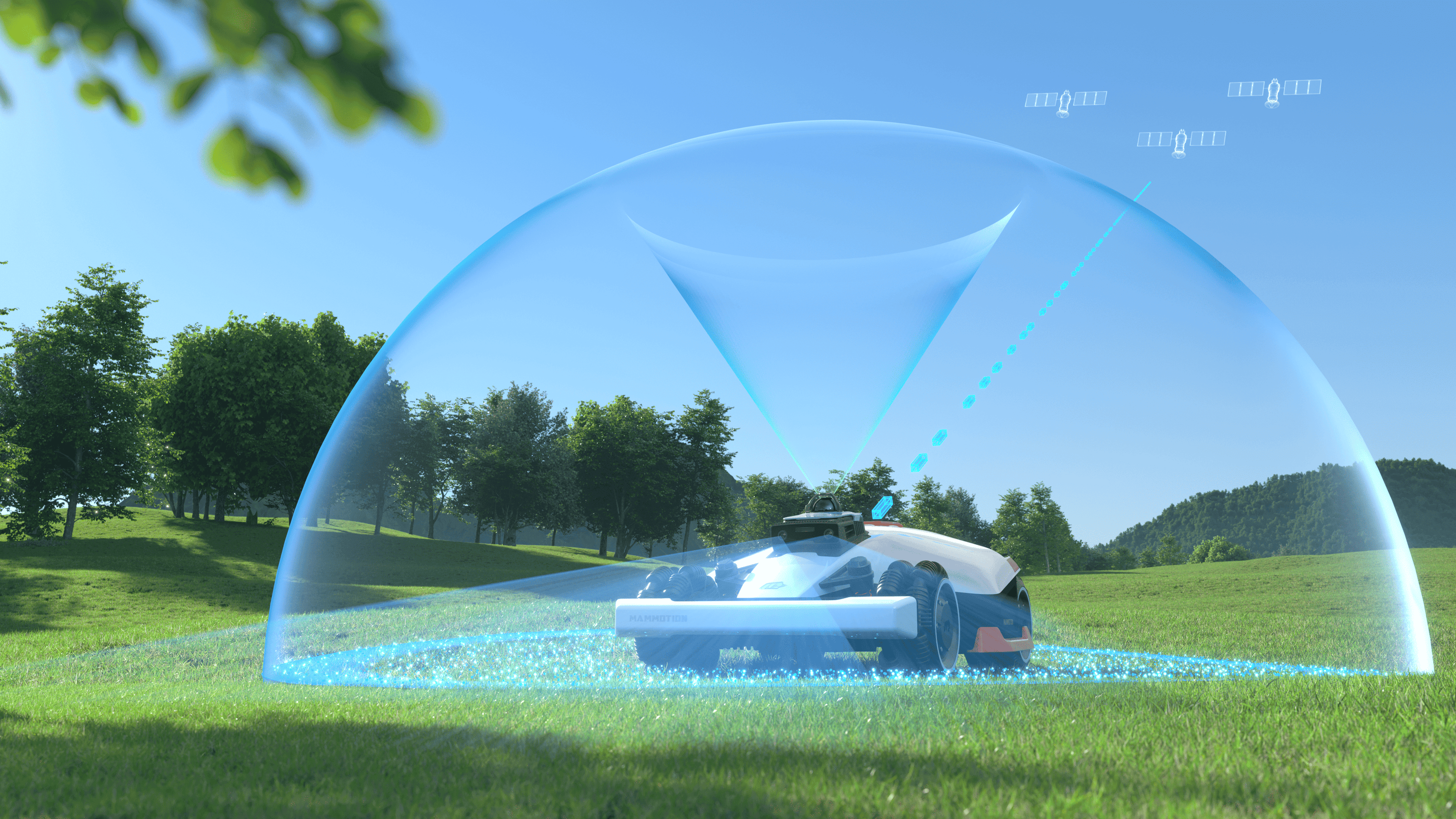
As robotic lawn mowers move beyond perimeter wires and simple navigation rules, AI vision technology has become one of the most critical components driving true autonomy. Unlike GPS or boundary-based systems that focus on position, vision allows a robotic mower to understand what’s actually happening on the lawn in real time.
Using cameras combined with computer vision algorithms, modern robotic mowers can recognize grass edges, detect obstacles, and respond to dynamic elements such as pets, children, or garden furniture. In essence, AI vision transforms a mower from a machine that follows instructions into one that perceives, interprets, and decides.
This capability is especially important in real-world lawns, where lighting changes, objects move, and boundaries aren’t always clearly defined. In this article, we’ll explore how AI vision works in robotic lawn mowers, what it can—and can’t—do today, and why it plays a central role in the future of intelligent lawn care.
What AI Vision Really Means in Robotic Lawn Mowers
When manufacturers talk about “AI vision,” they’re not simply referring to a camera mounted on a mower. In robotic lawn mowers, AI vision is a complete perception system that combines image capture, real-time processing, and machine learning to interpret the environment.

At the hardware level, vision systems use monocular, stereo, or 3D cameras positioned to see the lawn ahead of the mower. These cameras continuously capture visual data as the mower operates. That data is then processed locally by onboard AI chips—often referred to as edge AI—to avoid delays that cloud processing would introduce.
The real intelligence comes from computer vision models trained to recognize patterns: grass versus pavement, solid obstacles versus passable areas, and static objects versus moving ones. Instead of reacting blindly, the mower makes contextual decisions—slowing down near obstacles, rerouting around unexpected objects, or adjusting its path at lawn edges.
In simple terms, GPS tells a mower where it is. AI vision tells it what it’s dealing with. That distinction is what enables truly autonomous, wire-free mowing in unpredictable, real-world yards.
Core Functions Powered by AI Vision Technology of Robot Mower
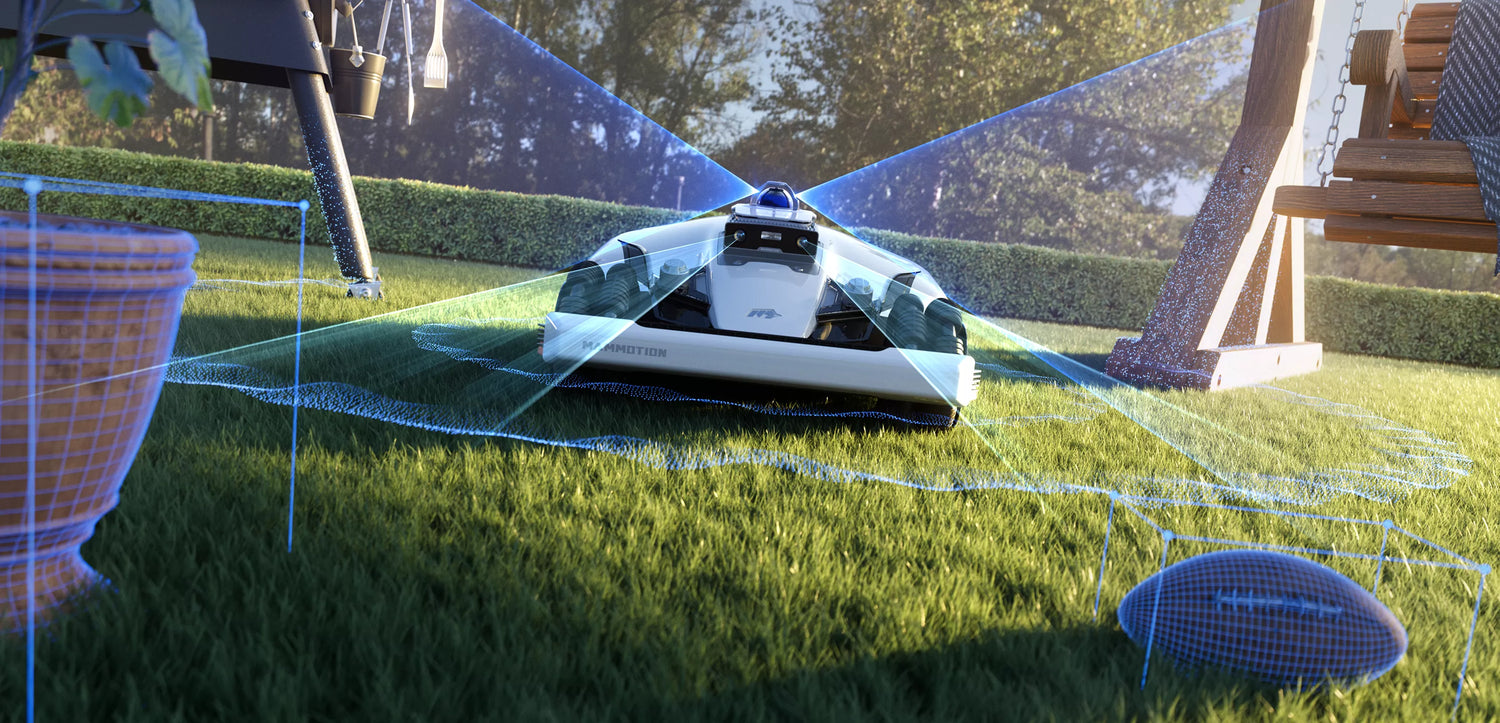
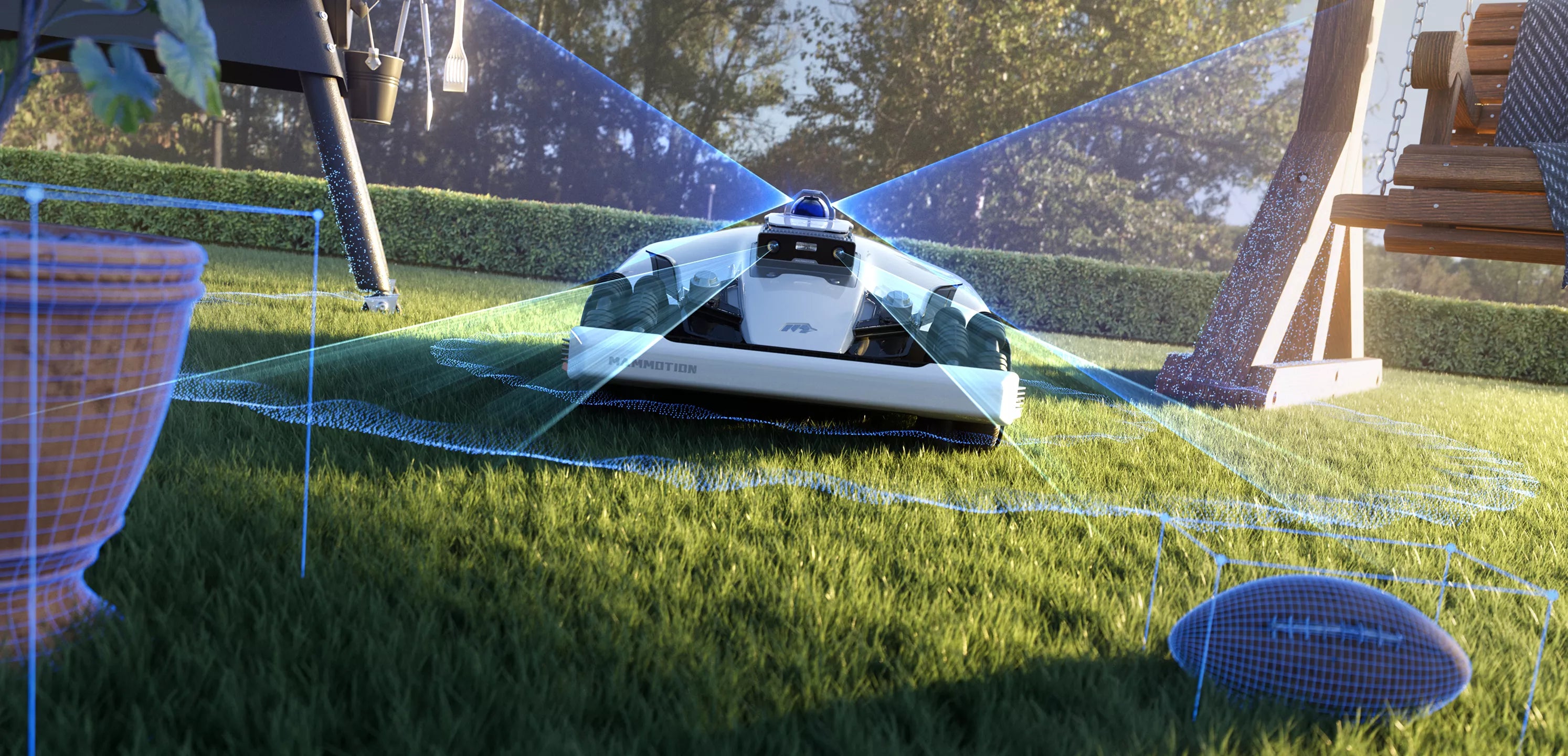
AI vision technology is not a single feature but a foundation that enables multiple intelligent behaviors. In robotic lawn mowers, vision systems work continuously to interpret the environment and support safe, efficient, and precise mowing decisions.
1. Lawn Edge and Boundary Recognition
One of the most important roles of AI vision is identifying where mowing should—and should not—occur. By analyzing visual cues such as color, texture, and surface continuity, vision systems can distinguish grass from non-grass areas like pavement, mulch, or flowerbeds.
This capability allows robotic lawn mowers to:
- Follow natural lawn edges without physical wires
- Navigate irregular boundaries with higher precision
- Adapt to subtle changes in lawn layout over time
Unlike fixed boundary systems, vision-based edge recognition can respond dynamically to real-world conditions.

2. Obstacle Detection and Classification
Not all obstacles are equal, and AI vision technology allows robot mowers to understand that difference.
- Through trained object-recognition models, vision systems can identify:
- Living obstacles such as pets or wildlife
- Temporary objects like toys, hoses, or garden tools
- Permanent features including trees, posts, and outdoor furniture
By classifying obstacles rather than simply detecting them, the mower can choose appropriate responses—slowing down, rerouting, or stopping entirely—improving both safety and efficiency.
3. Dynamic Object Tracking
Real-world lawns are not static environments. Children play, pets move unpredictably, and objects may enter the mowing area unexpectedly.
- AI vision enables robotic mowers to:
- Track moving objects in real time
- Predict motion paths over short distances
- Adjust speed and direction proactively
This dynamic awareness is essential for safe autonomous operation, especially in residential settings.
4. Surface and Terrain Awareness
Beyond obstacles, AI vision also contributes to understanding surface conditions. By analyzing visual patterns and shadows, some systems can infer uneven terrain, slopes, or transitions between surfaces.
This allows the robot lawn mower to:
- Adjust speed on slopes
- Improve traction management
- Maintain a more consistent cutting pattern
While vision alone does not replace physical sensors, it significantly enhances the mower’s ability to operate smoothly across varied terrain.

AI Vision vs Other Navigation Technologies in Robotic Lawn Mowers
AI vision is a powerful capability, but it does not operate in isolation. Modern robotic lawn mowers often combine vision with other navigation technologies to balance precision, reliability, and environmental adaptability. Understanding how AI vision compares to — and complements — these systems helps clarify its real-world role.
1. AI Vision vs RTK GPS
RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) GPS provides centimeter-level positioning by correcting satellite signals with reference data.
- RTK excels at answering one question: Where is the mower?
RTK offers high positional accuracy in open areas and struggles under trees or near buildings
- AI vision answers a different one: What is around the mower?
AI vision excels at obstacle detection and contextual understanding, and its performance depends on lighting and visual clarity
- Used together, vision adds environmental awareness to RTK’s positional precision.
2. AI Vision vs LiDAR
LiDAR uses laser pulses to measure distances and build 3D maps of the environment. It is extremely effective at detecting shapes and structures, regardless of lighting conditions.
- LiDAR detects objects but doesn’t inherently understand what they are, and excels in geometric accuracy
- AI vision provides semantic recognition — identifying pets, toys, or people, and excels in interpretation and decision-making
These technologies are complementary rather than competitive.
3. Pure AI Vision vs Sensor Fusion Systems
Some robotic mowers rely primarily on vision, while others combine vision with RTK, LiDAR, or both. Now Mammotion mixed these three technologies and called it the Tri-Fusion Positioning System, which can auto switch according to the mowing situation.
- Pure vision systems offer simpler setups and lower hardware complexity
- Sensor fusion systems deliver higher reliability across diverse conditions. AI Vision often serves as the decision layer, while other sensors provide spatial grounding
In practice, the most advanced robotic lawn mowers treat AI vision as the intelligence layer that makes sense of data from all sensors. (AI Vision vs. RTK vs. LiDAR: Which Robot Lawn Mower Navigation Technology is Right for You?)
Real-World Challenges of AI Vision in Robotic Lawn Mowers
While AI vision technology enables remarkable autonomy for robot lawn mowers, it is not without limitations. Understanding these challenges helps homeowners set realistic expectations and ensures safer, more effective operation.
1. Lighting and Weather Dependence
Vision-based systems rely on visible light, which makes them sensitive to environmental conditions:
- Low light or night operation can reduce detection accuracy unless additional illumination is provided
- Shadows and glare can confuse the system, potentially misclassifying obstacles or lawn edges
- Rain, fog, or snow may obscure visual cues, limiting performance
Advanced systems partially mitigate this by fusing vision with other sensors, but pure vision mowers remain vulnerable to environmental variability.
2. Seasonal and Surface Variations
AI vision interprets patterns and colors to distinguish grass from non-grass surfaces. However:
- Changes in grass color (e.g., drought, seasonal browning) can reduce edge detection accuracy
- Fallen leaves, mulch, or debris may be misinterpreted as obstacles
- Newly landscaped or uneven areas may require recalibration
Continuous learning and software updates improve performance over time, but occasional manual intervention may still be needed.
3. Dynamic and Unpredictable Obstacles
While vision systems can track moving objects, highly unpredictable situations remain challenging:
- Rapidly moving children or pets in the mowing path
- Objects that appear suddenly, like toys blown by wind
- Overlapping objects that obscure each other
Even advanced AI vision systems must slow or stop in uncertain situations to ensure safety.
4. Hardware Limitations
The performance of AI vision is also tied to the quality of the camera and onboard processor:
- Lower-resolution cameras may miss small obstacles
- Limited processing power can reduce real-time responsiveness
- Over time, camera lenses may become dirty or scratched, affecting detection
Routine maintenance and high-quality sensors are essential for a robot mower’s optimal performance.
AI Vision in Hybrid Navigation Systems of Robot Mowers
To overcome the limitations of pure vision, many modern robotic lawn mowers combine AI vision with additional navigation technologies such as RTK GPS and LiDAR. This approach, often called sensor fusion, leverages the strengths of each system to deliver more reliable and precise autonomous mowing.
1. AI Vision + RTK GPS
Combining AI vision with RTK GPS provides both contextual awareness and precise positioning:
- RTK GPS ensures centimeter-level accuracy in tracking the mower’s location
- AI vision interprets the surroundings, detects obstacles, and identifies lawn edges
- Together, the system can autonomously navigate complex layouts while maintaining efficiency
This hybrid setup is particularly useful in open lawns with occasional obstacles, ensuring the mower stays on track even in areas where GPS alone could drift.
2. AI Vision + LiDAR
Integrating LiDAR with AI vision enhances spatial perception and object recognition:
- LiDAR builds a dense 3D map of the environment, accurately measuring distances to objects
- AI vision adds semantic understanding, identifying objects as pets, toys, trees, or furniture
- This combination enables safe navigation in cluttered, shaded, or irregularly shaped yards
LiDAR provides geometric precision, while vision provides decision-making intelligence — a synergy that pure vision or LiDAR alone cannot achieve.
3. Tri-Fusion and Advanced Systems
Some of the latest robotic mowers, such as those using Mammotion’s Tri-Fusion navigation, combine AI vision, LiDAR, and RTK GPS into a single platform:
- Each sensor compensates for the others’ limitationso
- Vision handles object classification and context
- LiDAR provides 3D spatial mapping
- RTK GPS maintains precise global positioning
The result is a mower capable of handling complex, dynamic lawns with high reliability, reduced human intervention, and consistent cutting performance.
Conclusion: AI Vision as the Brain of Robotic Lawn Mowers
AI vision technology has redefined what robotic lawn mowers can do. By enabling machines to see, interpret, and make decisions, vision systems go far beyond simple navigation, allowing mowers to handle obstacles, adapt to complex landscapes, and maintain lawns with unprecedented precision.
While pure vision systems face challenges—such as lighting conditions, seasonal changes, and dynamic obstacles—combining AI vision with technologies like RTK GPS and LiDAR creates hybrid systems capable of safe, reliable, and fully autonomous operation. Vision acts as the decision-making layer, transforming sensor data into intelligent action.
In short, AI vision is not just a feature—it is the brain of AI robotic lawn mowers, shaping the future of intelligent, wire-free lawn care.